The body fat percentage is a key indicator of a person's health and overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explain the fundamentals of body fat percentage, its significance, and effective strategies for achieving a healthy body fat percentage.
This article is intended for anyone interested in the topic of body fat percentage and wishing to learn more about it.
Fundamentals of body fat percentage

Definition of body fat
Body fat is the adipose tissue present in our bodies. It primarily consists of fat cells, known as adipocytes. Body fat can be divided into essential fat and storage fat, depending on its function and location.
Functions of body fat in the body
Body fat serves several important functions in the body, including:
Energy storage
Fat is an efficient storage of energy, which can be utilised by the body when needed.
Thermal insulation
Adipose tissue insulates the body and helps regulate body temperature.
Protection of internal organs
Adipose tissue acts as a cushion protecting the internal organs from shocks and injuries.
Hormone production
Adipose tissue produces hormones such as leptin, which regulates food intake and body weight.
Distinguishing between essential fat and storage fat
Fat is not just fat. There is a significant difference between essential fat and storage fat.
Essential fat
Essential fat is the fat our body needs to function normally and remain healthy. It is present in various organs and tissues, such as in nerve cells, bone marrow, internal organs, and membranes.
Essential fat plays a crucial role in hormone production, thermal insulation, protection of internal organs, and maintenance of cell structure.

In men, the essential fat percentage is about 2-5%, while in women it is about 10-13%, as women require additional fat for reproductive functions.
Storage fat
Storage fat, on the other hand, is the fat that accumulates in fat cells under the skin (subcutaneous fat) and around the internal organs (visceral fat). This fat serves as an energy reserve and is broken down and burned by the body in times of increased energy demand.
A healthy amount of storage fat is important for overall well-being and energy supply, but too much storage fat can lead to health risks
Factors influencing body fat percentage
A person's body fat percentage is influenced by several factors, including:
Age
The body fat percentage generally increases with age.
Sex
Women tend to have a higher body fat percentage than men, as they require a higher proportion of essential fat.
Genetics
A person's genetic makeup can lead to them having more or less body fat.
Diet and physical activity
A balanced diet and regular physical activity can help control body fat percentage.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes in the body can influence body fat percentage, such as during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
Stress
Chronic stress can increase body fat percentage as it affects the production of stress-related hormones like cortisol, which favour fat accumulation.

Since body fat percentage is an important health indicator, it is essential to keep an eye on it and take action if necessary to maintain it at a healthy level.
In the following sections of this blog post, we will discuss various methods for measuring body fat percentage, recommendations for an optimal body fat percentage, and strategies for reducing body fat percentage.
Measuring body fat percentage
Accurate measurement of body fat percentage is crucial for monitoring progress towards achieving a healthy body fat percentage and assessing the effectiveness of applied strategies.
Various methods for measuring body fat percentage
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA)
This method measures the body's resistance to a weak electric current. Since adipose tissue has a higher resistance to electrical current than muscles and water, the body fat percentage can be calculated based on the measured resistance.
The accuracy of this method can be influenced by factors such as hydration status, recently consumed meals, and physical activity. Nonetheless, it is a simple, quick, and inexpensive way to measure body fat percentage.
Skinfold measurement
This method involves measuring the thickness of the skinfold at various body sites with a special caliper. The results are then input into a formula to estimate body fat percentage. The accuracy of this method depends on the examiner's experience and the consistency of the measurements.
While skinfold measurement may not be as accurate as other methods, it is a practical and inexpensive option. Nonetheless, it is a simple, quick, and inexpensive way to measure body fat percentage.
Hydrostatic weighing

The hydrostatic weighing method, also known as underwater weighing, is a more accurate method for measuring body fat percentage. In this method, the body is fully submerged underwater, and its buoyancy is measured.
Since fat is lighter than water and muscles are heavier, the body fat percentage can be calculated from the ratio of body weight to body volume. This method requires special equipment and expertise and is more expensive than BIA and skinfold measurement but provides more accurate results.
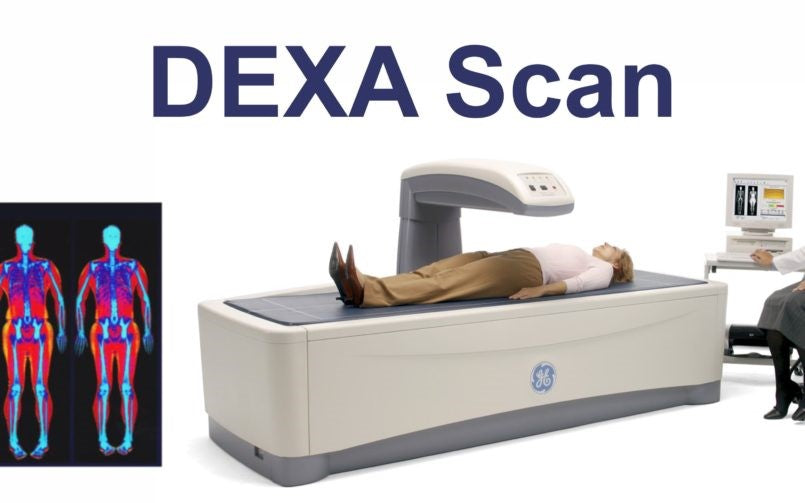
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
DEXA is a highly precise imaging technique that uses X-rays of two different energies to measure body fat percentage, bone mass, and lean mass. During the examination, the patient lies on a table while a scanner moves over the body, creating detailed images.
This method is very accurate and can also measure regional fat distribution, but it is more expensive and less accessible than the other methods. It also involves a small amount of radiation exposure, which is significantly lower compared to other imaging techniques such as CT scans.
Recommendations for most common use cases
For most people, BIA and skinfold measurement are sufficient to obtain an estimate of body fat percentage and track changes over time.
Both methods are inexpensive, easily accessible, and simple to perform. However, it is important to note that their accuracy depends on various factors and they may not provide the most precise results.
For individuals participating in scientific studies, athletes, or those requiring a very accurate measurement of their body fat percentage, hydrostatic weighing or DEXA may be considered.
These methods are more expensive and less practical but offer higher accuracy and provide additional information about body composition and bone mass.
When choosing a method for measuring body fat percentage, factors such as accuracy requirements, cost, accessibility, and personal preferences should be considered. Regardless of the chosen method, it is important to measure body fat percentage regularly to assess the progress and effectiveness of applied nutrition and training strategies.
In the next section of this article, we will discuss recommendations for an optimal body fat percentage and strategies for reducing body fat percentage to achieve a healthy body weight and good physical condition.

Optimal body fat percentage and health risks
A healthy body fat percentage is crucial for overall well-being and health. It is important to regularly measure body fat percentage to monitor progress and make adjustments as necessary.
A combination of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle can help maintain body fat percentage at an optimal level and minimise the risk of health problems. If you have any questions or concerns, it is advisable to consult a doctor or nutrition expert.
Recommendations for a healthy body fat percentage by sex and age
The optimal body fat percentage varies depending on sex, age, and individual factors. Generally, the following recommendations apply:
Body fat percentage for men
| Age group | Good | Average | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-24 Years | 8-12% | 13-17% | 18-22% |
| 25-34 Years | 10-15% | 16-20% | 21-25% |
| 35-44 Years | 12-17% | 18-22% | 23-27% |
| 45-54 Years | 14-19% | 20-24% | 25-29% |
| 55-64 Years | 16-21% | 22-26% | 27-31% |
| 65+ Years | 18-23% | 24-28% | 29-33% |
Body fat percentage for women
| Age group | Good | Average | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-24 Years | 16-20% | 21-25% | 26-30% |
| 25-34 Years | 18-22% | 23-27% | 28-32% |
| 35-44 Years | 20-24% | 25-29% | 30-34% |
| 45-54 Years | 22-26% | 27-31% | 32-36% |
| 55-64 Years | 24-28% | 29-33% | 34-38% |
| 65+ Years | 26-30% | 31-35% | 36-40% |
It is important to note that these values are only guidelines and individual differences should be considered. If in doubt or if you have health concerns, it is advisable to consult a doctor or nutrition expert.
Risks of high body fat percentage
Health consequences
A high body fat percentage can lead to various health problems, such as:
i) Cardiovascular diseases: Excess body fat can lead to increased blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
ii) Type 2 diabetes: Overweight and obesity increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes as they impair insulin sensitivity.
iii) Sleep apnoea: Excess adipose tissue in the throat area can block the airways and lead to sleep apnoea.
iv) Joint problems: Overweight places a strain on the joints and can lead to arthritis and other joint problems.
Psychological consequences
A high body fat percentage can also have psychological effects, such as: i) Self-esteem: Overweight individuals may suffer from low self-esteem due to their body image.
ii) Depression: There is a link between obesity and depression, with some studies showing that overweight individuals have a higher risk of depression.
Risks of low body fat percentage
Hormonal disturbances
A low body fat percentage can impair the production of hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, leading to infertility, irregular menstrual cycles, and bone loss.
Weakening of the immune system
A too low body fat percentage can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infections and diseases.
Impairment of body temperature regulation
Since adipose tissue contributes to thermal insulation, a too low body fat percentage can impair the body's ability to regulate its temperature, leading to decreased cold tolerance and increased risk of hypothermia.
Strategies for reducing body fat percentage
Dietary changes
a) Calorie Intake and Expenditure: To reduce body fat, it is important to achieve a caloric deficit. This means consuming fewer calories than you expend. The exact number of calories needed depends on factors such as age, sex, weight, and activity level.
b) Macronutrient Distribution (Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates): A balanced distribution of macronutrients is crucial for healthy weight loss. Generally, proteins should make up 25-30% of daily calorie intake, fats 20-35%, and carbohydrates 45-60%.
c) Importance of Micronutrients: Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are also important for overall health and metabolism. A varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources helps meet the need for micronutrients.

d) Recommendations for Healthy Foods: The following foods should be included in the diet to ensure a balanced nutrient supply:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains (e.g., oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Lean protein (e.g., chicken, fish, legumes)
- Healthy fats (e.g., avocado, nuts, olive oil)
- Low-fat dairy products (e.g., yoghurt, cheese)
Regular physical activity
a) Endurance Training (Cardio): Cardio exercises, such as running, cycling, or swimming, are important for improving overall endurance and burning calories. It is recommended to perform at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of intense endurance training per week.
b) Strength Training: Strength training helps maintain and increase muscle mass, which boosts metabolism and aids in reducing body fat. It is recommended to perform at least two strength training sessions per week, targeting all major muscle groups.
c) Importance of Recovery and Sleep: Adequate rest and sleep are crucial for the body's regeneration and the success of training. It is recommended to get at least 7-9 hours of sleep per night and allow sufficient recovery time after intense training sessions.
Lifestyle changes
a) Stress Management: Chronic stress can make fat loss more difficult and favour fat accumulation. Therefore, it is important to develop effective stress management strategies such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or relaxation techniques.
b) Support from Friends and Family: The support of friends and family can be crucial for success in losing weight. Share your goals and progress with your social circle to promote accountability, motivation, and support.
c) Realistic Goal Setting and Success Measurement: Set realistic goals for reducing your body fat percentage and regularly check your progress. Use various methods to measure your success, such as regular weighing, measuring waist circumference, or documenting your athletic performance.
Nutritional supplements
Nutritional supplements, also known as nutraceuticals, can play a complementary role in reducing body fat. It is important to emphasise that these substances alone are not sufficient to significantly reduce body fat. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and a balanced lifestyle are crucial factors for successfully reducing body fat percentage.

Some nutraceuticals that can contribute to reducing body fat include:
Green Tea Extract: Green tea is rich in antioxidants and contains natural compounds like catechins, which can boost metabolism and promote fat burning.
L-Carnitine: This amino acid plays a key role in fat metabolism, as it transports fatty acids into the mitochondria of cells, where they are burned for energy production.
Garcinia Cambogia: This tropical fruit extract contains hydroxycitric acid (HCA), which may promote fat loss and reduce appetite.
Chitosan: Chitosan is a fibre derived from the shell of crustaceans. It can help reduce fat absorption in the digestive tract by binding fat and excreting it from the body.
Tyrexin contains a combination of the above ingredients. It combines the benefits of green tea extract, L-carnitine, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), Garcinia Cambogia, and chitosan in a dietary supplement. The synergy of these ingredients can help support metabolism, promote fat burning, and reduce appetite, contributing to a more effective reduction in body fat percentage.
Nonetheless, it is important to remember that nutritional supplements like Tyrexin alone are not sufficient to significantly reduce body fat. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and a balanced lifestyle are crucial factors for the successful reduction of body fat percentage.
Summary
The journey to reducing body fat percentage requires a combination of dietary changes, regular physical activity, and lifestyle adjustments. A balanced diet with an appropriate distribution of macronutrients, rich in micronutrients, forms the foundation for fat loss.
Regular endurance and strength training exercises contribute to calorie burning and muscle mass maintenance. Finally, lifestyle changes, such as stress management and social support, are crucial for long-term success. By setting realistic goals and regularly monitoring progress, you can successfully reduce your body fat percentage and lead a healthier life.

In conclusion, we would like to encourage you, dear readers, on your journey to a healthy body fat percentage. Every step towards a healthier lifestyle is a success. Remember to set realistic goals, regularly review your progress, and seek support from experts, friends, or family when needed.
Through continuous efforts and the implementation of the strategies described in this article, you will successfully reduce your body fat percentage and thus contribute to a healthier and happier life.